Greenhouse Gas On Steroids - Enter MethaneSat For The Fight
Chief Scientist at the Climate Institute in Washington DC and current Environmental Research Advocates Board Member Michael MacCracken's primary focus study to reduce precursors to tropospheric ozone will have an ancillary assist with the launch of MethaneSAT.
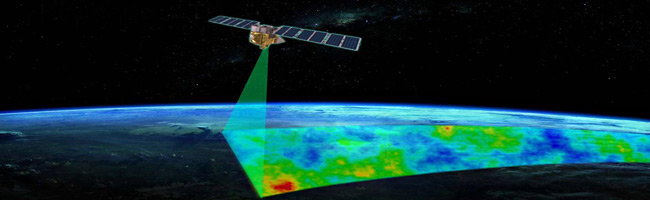
MethaneSAT is an Earth observation satellite that will monitor and study global methane emissions primarily in order to combat climate change. MethaneSAT is the first satellite of its kind which will measure methane pollution from oil and gas facilities worldwide with broad scope and exacting precision. It will orbit the Earth at 200-plus kilometers to have a large view path to quantify known sources, but also to discover and quantify previously unknown sources. It can also measure surface-level methane emissions from other major sources of human-caused methane emissions.
MethaneSAT is a mission jointly funded and operated by the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), an American non-governmental organization, and the New Zealand Space Agency. While most large-scale satellite projects from researchers and space-program organizations require multi-purpose platforms and private-sector ventures sell data to corporate and government agencies, MethaneSAT data will be available to everyone. It should be noted, this satellite project will be New Zealand's first entry into a space program.
With so much importance and information placed on CO2 emissions, the need to address methane in the atmosphere is much more critical. Methane is 85 times more powerful than carbon dioxide when it comes to planet-warming properties. Methane, being one of five man-made global greenhouse gasses, is an exceedingly effective greenhouse gas at trapping infrared radiation. The atmospheric residence time of methane is approximately 10 years. However, over a span of 100 years from continuous emissions, methane will be 28 times more effective than carbon dioxide in trapping heat and cause global warming on a grander scale -- it is considered the green house gas on steroids.
Reducing precursors to tropospheric ozone is now at a critical moment in history since global warming is identified as a direct reaction to active ozone formations in the atmosphere. The majority of tropospheric ozone formation occurs when nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH4) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), react in the atmosphere in the presence of sunlight, specifically the UV spectrum.
MethaneSAT will provide data much quicker than prior technologies, to assist scientists, researchers and, hopefully, industrialists to reduce methane emissions to help slow the consequences of global warming.
Sources:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MethaneSAT
https://www.edf.org/climate/how-methanesat-is-different
https://climateaccountability.org/pdf/MacCracken%20Bio%20Jul13.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ground_level_ozone
Image courtesy of Environmental Defense Fund, edf.org.
