TEG - The Hope and Future of the Human Race

 Many credible environmentalists and scientists agree society needs to be less reliant on petroleum and the grid. As a world consortium, we all realize the dependence the human population has on non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels that power 80% to 90% of all humankind's energy needs. Aside from inevitable depletion of natural non-renewable resources and the destruction to the planet's eco-system, current energy systems cannot sustain a growing population indefinitely. The solution is the human population itself; why not use the human body as that alternative renewable energy source we all will eventually need?
Many credible environmentalists and scientists agree society needs to be less reliant on petroleum and the grid. As a world consortium, we all realize the dependence the human population has on non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels that power 80% to 90% of all humankind's energy needs. Aside from inevitable depletion of natural non-renewable resources and the destruction to the planet's eco-system, current energy systems cannot sustain a growing population indefinitely. The solution is the human population itself; why not use the human body as that alternative renewable energy source we all will eventually need?
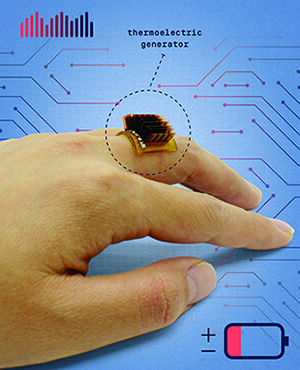
Enter TEG. Thermoelectric generators (TEG) is a technology that converts heat into electrical current. Jianliang Xiao, an associate professor at the Paul M. Rady Department of Mechanical Engineering at CU Boulder, has developed a wearable mini TEG that can stretch from a ring to a bracelet converting low-grade heat emitted from the human body into renewable electricity.
Xiao's wearable mini-thermoelectric generator (TEG) can generate about 1 volt of energy for every square centimeter of skin space, powering small devices such as watches, Fitbits, LED lights and other low-capacity devices. Modular stacking of TEG(s) can provide more voltages as needed.
The TEG is composed of modular thermoelectric chips, liquid metal as electrical wiring, and dynamic covalent thermoset polyimine as both the substrate and encapsulation for liquid-metal wiring. The stretchy polyimine has self-healing properties in case of tear damage. All parts of the TEG are recyclable, given that its development was engineered for environmental concerns as well. TEG technology may even cause the battery to become obsolete!
So much energy is wasted from the human body, in truth we are the most inefficient mammal on planet earth. However harnessing our own body heat to generate power for devices we normally carry, such as mobile phones, watches, health monitoring devices, radios, pace-makers, and hearing aids, can help reduce human dependence on finite power sources.
Sources:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abe0586
https://www.colorado.edu/today/2021/02/10/thermoelectric
https://www.popularmechanics.com/science/a35533572/body-heat-battery/
Thermoelectric illustration courtesy of Popular Mechanics, illustrated by Alyse Markel using photo courtesy Xiao Lab.
"Let there be Lightbulb" image by Will J (courtesy of Zumwinkle.com).
